Details of Genipin:
|
Botanical Source |
It is an aglycone derived from an iridoid glycoside called geniposide present in fruit of Gardenia jasminoides,Rubiaceae. |
|
CAS NO. |
6902-77-8 |
|
Analysis |
HPLC |
|
Specification |
95%,98% ,99% |
|
Function |
|
|
Genipin is an excellent natural cross-linker for proteins, collagen, gelatin, and chitosan cross-linking.
The beneficial actions of genipin emerge from a number of research projects in the areas of the therapies of diabetes, periodontitis, cataract, hepatic dysfunction, as well as in wound repair and nerve regeneration. |
|

Sources of Genipin
It is an aglycone derived from an iridoid glycoside called geniposide present in fruit of Gardenia jasminoides,Rubiaceae,which is included in Chinese Pharmacopea .It is an evergreen shrub that grows four to eight feet tall and wide. The fruit of Gardenia jasminoides has been used as a tradition Chinese medicine to treat irritability in febrile diseases, jaundice, acute conjunctivitis, epistaxis, hematemesis, pyrogenic infections and ulcers of the skin, and externally on sprains and painful swelling due to blood stasis,The fruit are oval in shape about one-half inch to one inch long and orange in color. The gardenia fruit is approved to be used in food by Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China.Studys shows it may be used in curing hepatitis, hypertension,diabetes,etc.
Ingredients of Genipin
Geniposide, an iridoid glucoside, is a major constituent in the fruits of Gardenia jasminoides (Gardenia fruits), a popular Chinese herb. Genipin, the aglycone of geniposide,is used to prepare blue colorants in food industry and also a crosslinking reagent for biological tissue fixation 1. It is soluble in methanol,ethanol,actone,ethyl-acetate etc.Genipin is a white crystal.
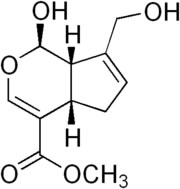

Specification of Genipin
|
ITEMS |
SPECIFICATION |
|
Appearance |
White crystalline powder |
|
Purity (HPLC) |
Not less than 98.0%(dried basia) |
|
Loss on Drying |
≤2.0% |
|
Melt point |
120-122℃ |
|
Heavy Metal |
<20ppm |
|
As |
<2ppm |
|
Lead(pb) |
<2ppm |
|
Residual Solvent |
Eur.Pharm |
|
Microbiology |
|
|
Total Plate Count |
<1000cfu/g |
|
Yeast & Moulds |
<100cfu/g |
|
E.Coli |
Negative |
|
Salmonella |
Negative |
Study of Genipin
Natural Cross-Linker
Genipin is an excellent natural cross-linker for proteins, collagen, gelatin, and chitosan cross-linking.It has a low acute toxicity, with LD50 i.v. 382 mg/kg in mice, therefore, much less toxic than glutaraldehyde and many other commonly used synthetic cross-linking reagents.Furthermore, genipin can be used as a regulating agent for drug delivery, as the raw material for gardenia blue pigment preparation, and as the intermediate for alkaloid syntheses[1]。 Genipin in conjunction with chitosan are the preparation of elastic and resistant gels such as the cartilage substitutes, the manufacture of drug carriers for controlled release, the encapsulation of biological products and living cells, and the medication of wounds in animals and humans. Genipin might replace glutaraldehyde with the advantages of stability and biocompatibility of the crosslinked products whose quality assessment and manipulation would be easier[2]. The genipin-crosslinked casein hydrogel might be a suitable polymeric carrier for protein drug delivery in the intestine[3]
Pharmacological Study
Genipin, rather than geniposide, is the major anti-inflammatory component of gardenia fruit.Genipin, the aglycone of geniposide, is metabolically produced from the geniposide in body tissues[4].The beneficial actions of genipin emerge from a number of research projects in the areas of the therapies of diabetes, periodontitis, cataract, hepatic dysfunction, as well as in wound repair and nerve regeneration[5]
Toxicity Study
Genipin may have toxicity when it is administrated i,g to rat at high dose[6].Oral administration of 200 mg/kg of genipin resulted in a mortality of 78% (7/9) in rats[7].
![]()
Reference of Genipin
1 Zheng Li-sheng, Ni Na,LIU Xiang-qian,Chen Chang-qing,Study and application of geniposide and genipin Drug Evaluation Research, 2012,35(4):289-298
2 Riccardo,Muzzarelli,Genipin-crosslinked chitosan hydrogels as biomedical and pharmaceutical aidsCarbohydrate Polymers,2009,77(1): 1–9
3 Fei Song,Li-Ming Zhang,Chuan Yang,Genipin-crosslinked casein hydrogels for controlled drug delivery International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2009,373(1-2):41–47
4 Hye-Jin Koo,Yun Seon Song,Hee-Jeong Kimm,Antiinflammatory effects of genipin, an active principle of gardenia,European Journal of Pharmacology,2004,495(2-3): 201–208
5 Yang Yi-shun,Zhang Tong,Yu Shai-cheng,Study development and pharmacological value of genipin, Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine ,2011,33(1):130-133
6 Yang Hong-jun,Fu Hong-mei,Wu Zi-lun,etc,Liver toxicity study of Gardenia jasminoides in rats,Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicein,2006,31(13):1091-1093.
7 Hou Y C,Tsai S Y,Lai P Y,et al Metabolism and pharmaco-.kinetics of genipin and geniposide in rats[J]. Food Chem Toxi-col,2008,46:2764-2769.




